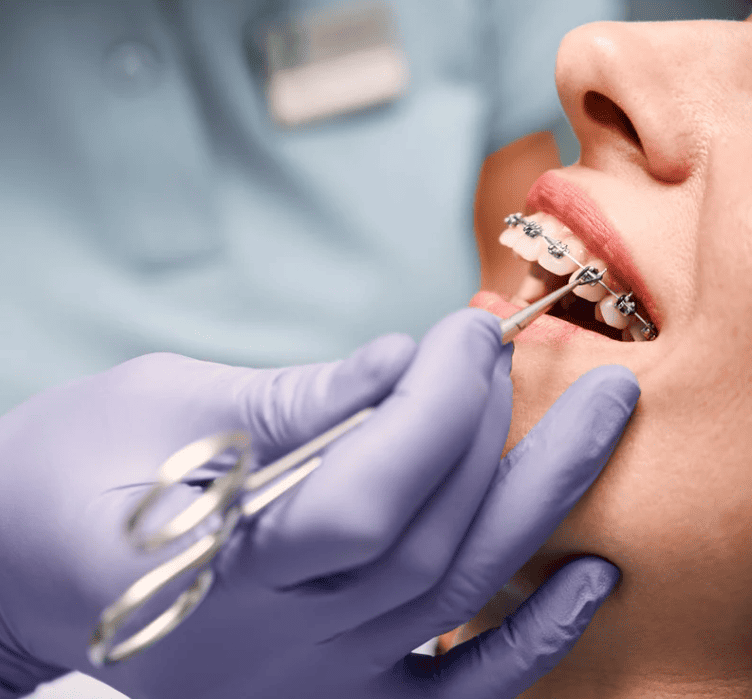
Understanding Gum Inflammation: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Gum inflammation is one of the most common oral health issues. Many assume it’s just “slightly swollen gums” or “bleeding when brushing”, but in fact, gum inflammation is often an early warning sign of gum disease (periodontal disease). If left untreated, it can lead to gum recession, loose teeth, and even tooth loss.
This article provides a complete guide to help you understand the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention of gum inflammation.
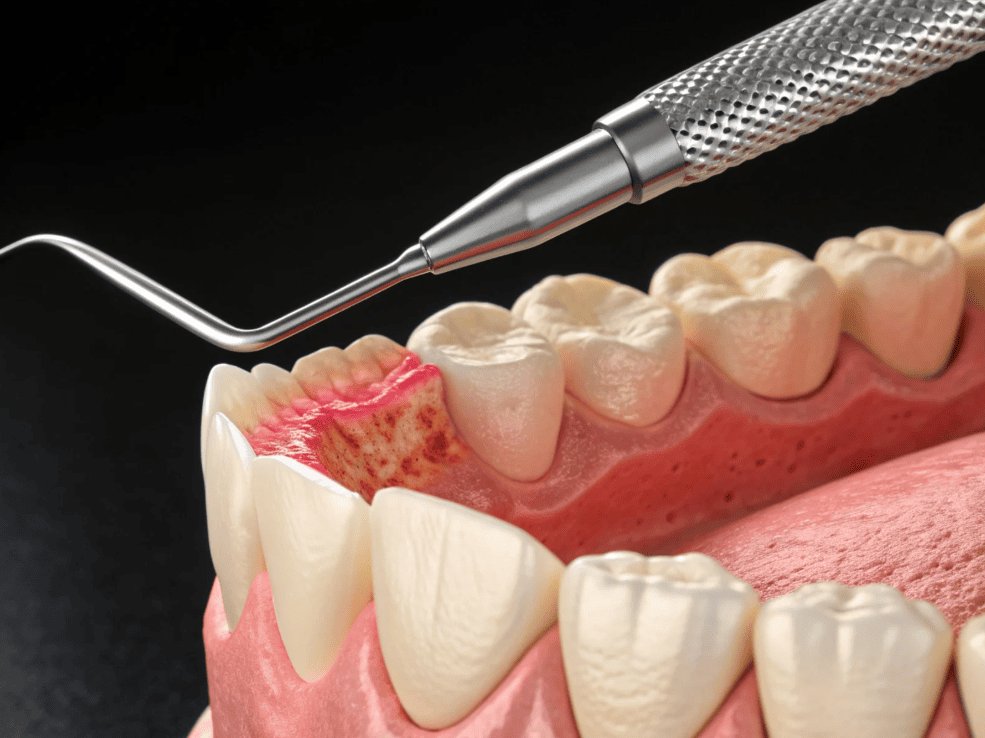
What Is Gum Inflammation?
Gum inflammation, also known as gingivitis, occurs when the soft gum tissue surrounding your teeth becomes infected or irritated by bacteria, leading to redness, swelling, tenderness, or bleeding. It represents the earliest stage of gum disease, and although common, it is frequently overlooked.
When dental plaque (a sticky film of bacteria) builds up around the gumline, the bacteria release toxins that irritate and damage the gum tissue. As a result, the gums may become swollen, sensitive, and bleed easily when brushing or flossing.
If ignored, the inflammation can progress deeper into the supporting structures of the teeth — affecting the tooth roots and jawbone — eventually developing into periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease that can cause tooth mobility or tooth loss.
Why Gum Inflammation Often Goes Unnoticed
In its early stages, gum inflammation is usually painless, so many people mistake it for a minor issue. You might notice your gums looking slightly red or bleeding a little after brushing, and think it’s nothing serious.
However, this is the best time to seek professional care. With early detection and proper cleaning, gum inflammation can be fully reversed before it develops into periodontal disease.
Common Areas Affected by Gum Inflammation
Gum inflammation can occur in different parts of the mouth, but it often affects the following areas:
- Gumline (near the base of the teeth): The most common site where dental plaque accumulates and irritates the gums.
- Gums behind the wisdom teeth: This area is difficult to clean, allowing food debris and bacteria to build up easily, leading to localised inflammation.
- Between teeth, around dental bridges or dentures: Artificial restorations can trap bacteria and plaque if not cleaned thoroughly, increasing the risk of infection.
Book Your Dental Check-up Today
No matter where you are in Hong Kong, we offer convenient and professional dental care. With five clinics located in Central, Tung Chung, and Discovery Bay, we make it easy for you to access trusted dental treatment.

We Accept Health Care Vouchers!
Smith & Jain Dentist
(Our Flagship)
Diestel & Partners
(Dental Surgeons)
Bayside Dental
Tung Chung
Bayside Dental Discovery Bay
North Plaza
Bayside Dental Discovery Bay
Main Plaza
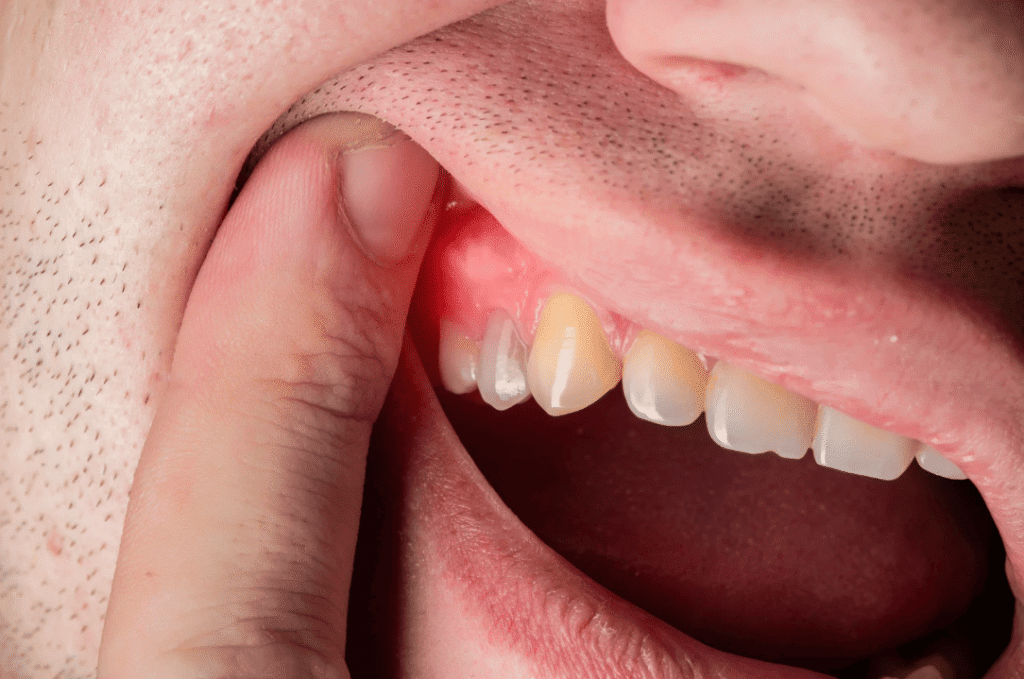
Causes of Gum Inflammation
The root cause of gum inflammation is almost always linked to bacterial infection and inadequate oral hygiene, but your daily habits and overall health also play a major role in determining gum health. Below are the five most common causes explained in detail:
🪥 1. Plaque and Tartar Build-Up
After every meal, bacteria in the mouth combine with food particles to form a sticky layer called dental plaque.
If not properly removed, this plaque can harden within 24–48 hours into tartar (calculus) — a rough, solid deposit that clings to the gumline.
Once tartar forms, it continually irritates the gums, leading to redness, swelling and bleeding.
💡 Dentist’s Tip: Brushing alone cannot remove tartar. It must be cleaned professionally through a dental scaling procedure carried out by a dentist or dental hygienist.
🍬 2. Poor Oral Hygiene Habits
Certain daily habits make it easier for bacteria to thrive and cause inflammation:
- Brushing for less than two minutes each time
- Neglecting to use dental floss or interdental brushes
- Using an old or hard-bristled toothbrush
- Skipping regular professional cleanings
Even if your teeth appear clean, plaque can still hide below the gumline, leading to chronic gum inflammation over time.
🦷 3. Periodontal Disease
If gum inflammation is left untreated, the infection may spread to the deeper supporting structures of the teeth — including the tooth roots, periodontal ligaments, and jawbone — resulting in periodontal disease.
At this stage, the gums begin to recede, exposing the tooth roots. You may notice loose teeth or changes in how your bite feels. Periodontal disease is chronic and irreversible, but with professional treatment and regular maintenance, the condition can be managed effectively to prevent further damage or tooth loss.
😷 4. Systemic Health Factors
Certain health conditions can make the gums more prone to bacterial infection and inflammation:
- Hormonal changes (during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause)
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled blood sugar weakens the immune system and slows healing
- Weakened immunity due to chronic stress or immunosuppressive medication
- Vitamin C deficiency, which can cause bleeding and swollen gums
💡 Dental Advice: Pregnant women and patients with diabetes should pay extra attention to gum care and schedule regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings to reduce their risk of infection.
🚬 5. Smoking Habits
Smoking is one of the highest risk factors for gum inflammation and periodontal disease. Nicotine affects the gums in several ways:
- Constricts blood vessels, reducing circulation to gum tissue
- Weakens the immune response, making infections harder to heal
- Masks symptoms such as bleeding, giving a false impression of healthy gums
Smokers are 2 to 3 times more likely to develop gum disease than non-smokers and often experience slower healing after treatment.
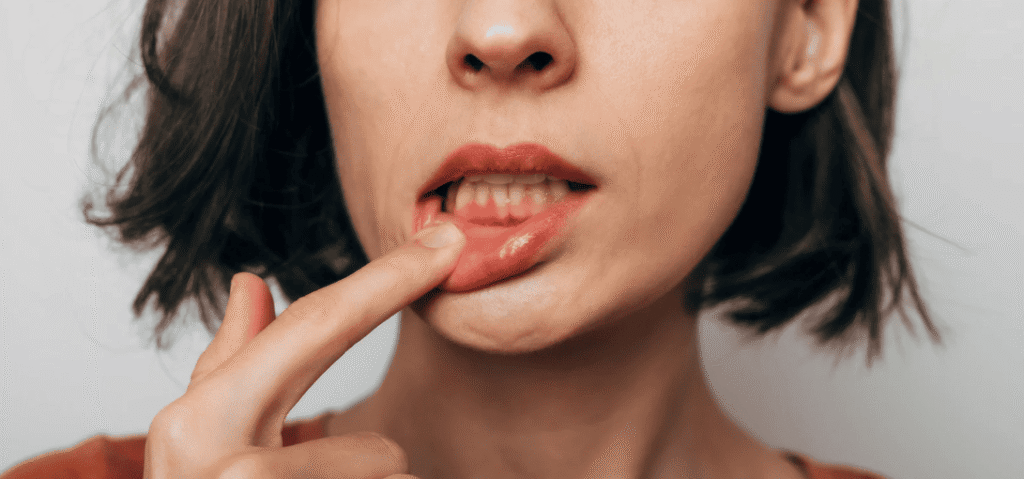

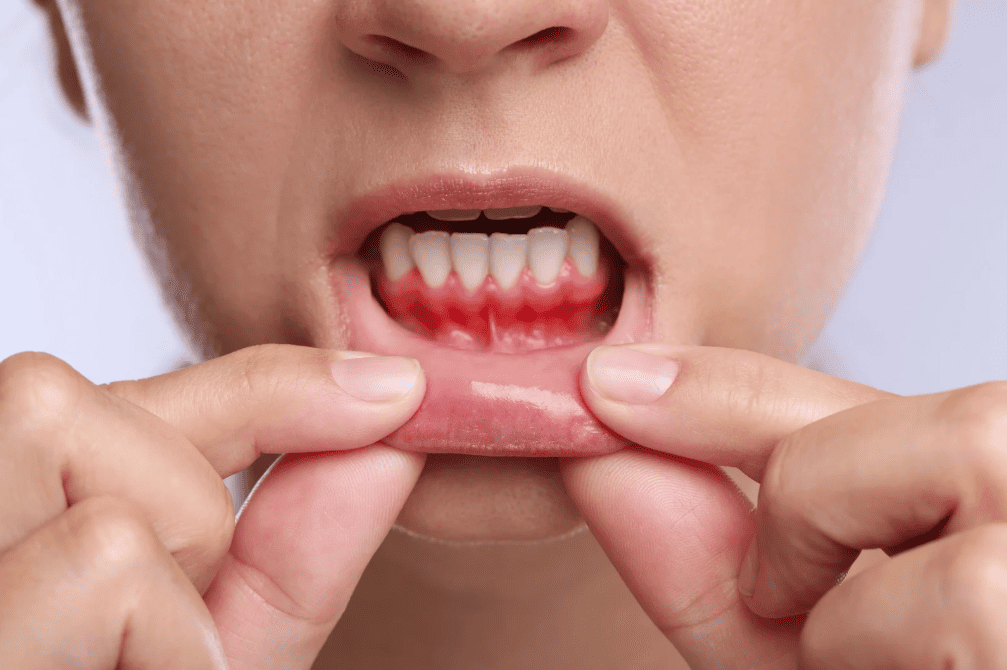
Symptoms of Gum Inflammation
In the early stages, gum inflammation often causes little to no pain — but it is one of the first warning signs that your gums are unhealthy. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s best to book a dental check-up as soon as possible to prevent the condition from progressing into periodontal disease.
| Symptom | Possible Cause & Dentist’s Explanation |
| Red or swollen gums | Usually caused by plaque or tartar buildup irritating the gum tissue, leading to mild pain or tenderness. If the area feels sore to touch, it may indicate a local infection. |
| Bleeding when brushing or flossing | A common sign of gingivitis or early gum disease. Healthy gums should not bleed — frequent bleeding means inflammation has already started. |
| Persistent bad breath or unpleasant taste | Bacteria accumulation and tartar deposits release volatile sulphur compounds, causing bad breath, especially noticeable in the morning or after meals. |
| Receding gums or teeth appearing longer | Indicates long-term inflammation and gum tissue loss, which may suggest chronic periodontitis. |
| Swelling or pain around wisdom teeth | Food debris easily gets trapped behind wisdom teeth, making the area difficult to clean and prone to local gum infection (commonly known as “wisdom tooth inflammation”). |
| Slight tooth mobility or bite discomfort | When inflammation persists, the periodontal ligament and bone support begin to deteriorate — a sign of moderate gum disease. |
| Dark red or purplish gum colour | Suggests poor circulation or chronic inflammation, often seen in smokers or long-term gum disease patients. |
💡 Dentist’s Advice
Early-stage gum inflammation can usually be completely reversed with professional dental cleaning and proper oral hygiene. However, if left untreated for too long, the inflammation may destroy the surrounding bone and gum structure — leading to irreversible damage.
What to Do If You Have Gum Inflammation?
The key to treating gum inflammation is to remove bacteria and tartar, control infection, and help the gums recover.
Depending on the severity of the inflammation, your dentist will design a personalised treatment plan to restore gum health.
🧼 1. Professional Dental Cleaning (Scaling)
This is the most common and effective first step in treating gum inflammation. During the procedure, your dentist or dental hygienist uses an ultrasonic scaler to remove tartar and plaque from the tooth surfaces and gumline, reducing irritation and inflammation.
- Best for: Gingivitis or mild gum disease
- Results: Reduces gum swelling and bleeding, improves breath freshness
- Recommended frequency: Every 6 months for maintenance
🦠 2. Deep Periodontal Cleaning (Root Planing)
If inflammation has spread deeper around the tooth roots, a simple cleaning may not be enough. Your dentist may recommend root planing, a deep cleaning procedure that removes bacteria and toxins from the tooth root surfaces and periodontal pockets.
- Best for: Early-stage periodontitis or gum recession
- Goal: Reduce pocket depth and promote gum reattachment
- Comfort: Can be performed under local anaesthesia for a pain-free experience
💊 3. Antibiotic or Anti-inflammatory Therapy
If the infection is more severe or an abscess is present, your dentist may prescribe:
- Antibiotics (oral tablets or topical gel)
- Antibacterial mouthwash (such as chlorhexidine rinse)
- Anti-inflammatory medication to relieve pain and control swelling
💡 These medications serve as supportive therapy and should always be combined with professional cleaning to fully resolve the problem.
🪥 4. Improve Daily Oral Hygiene Habits
After treatment, good daily care is essential to prevent recurrence. Here’s what dentists recommend:
- Brush twice daily for at least 2 minutes each time
- Use dental floss or interdental brushes to clean between teeth and along the gumline
- Choose fluoride toothpaste to strengthen enamel and prevent bacteria buildup
- Use antibacterial mouthwash to reduce plaque formation
- Visit your dentist or dental hygienist every 6 months for professional cleaning and gum health monitoring
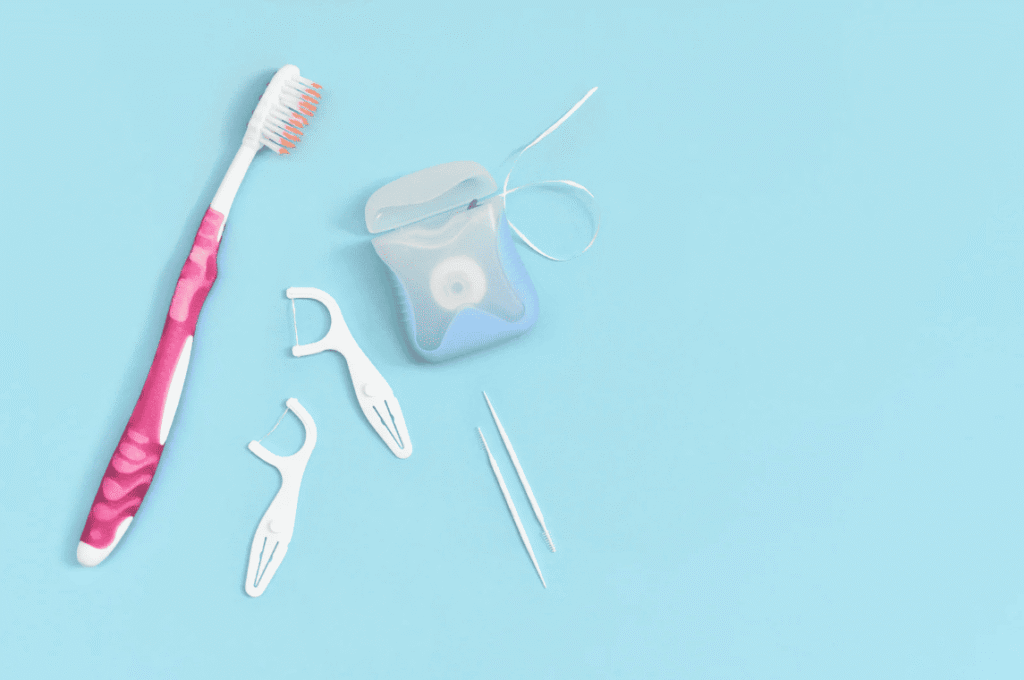
Daily Oral Care Habits to Prevent Gum Inflammation
Keeping your gums healthy isn’t difficult — it all comes down to consistent oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups.
Below are practical dentist-approved tips to help prevent gum inflammation and periodontal disease.
🦷 1. Brush Properly and Gently
Brush your teeth twice a day — once in the morning and once before bed — for about two minutes each time. Use the Bass brushing technique, holding the toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to the gumline and using gentle, small circular motions to remove plaque effectively.
Avoid brushing too hard or using stiff-bristled brushes, as these can lead to gum recession and enamel wear. It’s best to use a soft-bristled or electric toothbrush and replace it every three months.
🪥 2. Floss Daily to Clean Between Teeth
Even thorough brushing cannot remove all the plaque and food debris between teeth. Using dental floss or interdental brushes daily helps remove hidden bacteria, reducing the risk of gum swelling and bleeding.
💡 Dentist’s tip: If you have wider gaps between teeth, use interdental brushes instead of floss for more effective cleaning.
🥦 3. Eat a Balanced Diet to Support Gum Health
Nutrition plays an essential role in maintaining healthy gums.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks to reduce plaque formation.
- Increase your intake of vitamin C, vitamin D, and calcium, which help repair and strengthen gum tissue.
- Foods such as kiwi, oranges, leafy greens, and nuts are excellent choices for gum health.
🚭 4. Quit Smoking to Lower the Risk of Gum Inflammation
Smokers are more than twice as likely to develop gum inflammation compared to non-smokers. Nicotine constricts blood vessels and reduces gum blood flow, making inflammation harder to detect and delaying healing.
If you smoke, speak to your dentist about quitting support options to help restore gum health and improve treatment outcomes.
Related keywords: smoking and gum disease, nicotine gum effects, quit smoking oral health benefits
🩺 5. Schedule Regular Dental Cleanings and Check-Ups
If plaque isn’t removed properly, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a professional dental hygienist.
Dentists recommend professional scaling and oral examinations every 6 months to detect and prevent early signs of gum disease.
At Bayside Dental Discovery Bay, our experienced dental hygienist team provides gentle and thorough cleanings to help patients maintain long-term gum health.
⚠️ When Should You See a Dentist?
You should schedule a dental appointment immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Gum swelling or pain lasting more than one week
- Frequent bleeding when brushing or flossing
- Receding gums or teeth that feel slightly loose
- Persistent bad breath or mouth discomfort
- Pus formation or darkening of gum colour around teeth
These symptoms may indicate that gum inflammation has progressed into periodontitis, which requires professional dental treatment.
We offer comprehensive gum treatment and periodontal care, combined with routine dental cleaning and hygiene maintenance to help patients effectively manage inflammation and restore gum health.
Conclusion: Don’t Ignore Gum Inflammation — Early Treatment Is Key
Gum inflammation may seem minor at first, but if left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis and eventually lead to tooth loss.
By practising proper brushing techniques, maintaining a balanced diet, quitting smoking, and scheduling regular dental cleanings, you can effectively prevent gum problems before they worsen.
If you are experiencing red, swollen, or bleeding gums, we invite you to schedule a professional dental examination at Bayside Dental Discovery Bay.
Our dentists will assess your gum health and design a tailored treatment plan to help you regain a confident, healthy smile.
Book Your Dental Check-up Today
No matter where you are in Hong Kong, we offer convenient and professional dental care. With five clinics located in Central, Tung Chung, and Discovery Bay, we make it easy for you to access trusted dental treatment.

We Accept Health Care Vouchers!
Smith & Jain Dentist
(Our Flagship)
Diestel & Partners
(Dental Surgeons)
Bayside Dental
Tung Chung
Bayside Dental Discovery Bay
North Plaza
Bayside Dental Discovery Bay
Main Plaza
Gum Inflammation FAQ
1. What causes gum inflammation?
The main cause is plaque buildup — when bacteria accumulate along the gumline, it irritates the gums, leading to redness, swelling, and bleeding.
Other causes include improper brushing, smoking, hormonal changes, stress, poor nutrition, or systemic conditions such as diabetes.
2. Can gum inflammation heal on its own?
Mild inflammation may subside with proper brushing and flossing within a few days.
However, if symptoms like persistent swelling, bleeding, or gum recession occur, it’s important to visit a dentist promptly to prevent gum disease.
3. Which dental treatment is needed for gum inflammation?
You should see a dentist or dental hygienist for a professional cleaning.
If the infection has spread deeper into the gums, your dentist may recommend scaling and root planing or other periodontal treatments.
4. How can I prevent gum inflammation?
- Brush twice daily and floss every day
- Get professional teeth cleaning every 6 months
- Avoid smoking and limit sugar intake
- Maintain a balanced diet and adequate rest
- Pay extra attention to cleaning around braces or dental implants
5. What are the risks of untreated gum inflammation?
If left untreated, gum inflammation can progress to periodontal disease, leading to bone loss, loose teeth, or even tooth loss.
Chronic gum inflammation has also been linked to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and pregnancy complications.
Disclaimer
The information on the Bayside Dental Discovery Bay website is for general educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional dental diagnosis, advice, or treatment. Consult a licensed dentist for personalized dental care.
Bayside Dental strives to provide accurate information but does not guarantee its completeness or applicability to all circumstances. Bayside Dental Discovery Bay, including its Main Plaza and North Plaza clinics, is not liable for any damages resulting from the use of this website.
External links are provided for reference only. Bayside Dental is not responsible for the content or accuracy of third-party websites.